| |
BREASTS
WHAT IS NORMAL?
- Breasts look good if symmetric.
However, the left side is usually larger than the right.
- Size is subjective. The breast usually reaches the sixth rib. Average volume would be a B or C cup.
- Nipple is well above the fold and points outward. The skin color around the nipple (areola) usually takes up less than one-third of the breast surface.
- Overly large breasts can be a difficult problem,
both psychologically, as well as physically, causing
backaches, bra strap ulcerations etc..
COMMENT: Personal preference has a lot to do with breast aesthetics. SELF-EVALUATION:
- Is your breast volume and position adequate?
- Place a pencil underneath one breast. If the pencil holds, some form of lifting in addition to volume size may be recommended.
- Do you have back pain from breast mass?
- Are stretch marks present from alterations in breast size?
HOW MUCH CAN BE IMPROVED?
- Breast enlargement is usually performed by implants. Chest wall size and the amount of loose skin in which to place the implant are limiting. Usually, two increases in cup size is the
suggested maximum.
- Breast reductions often produce a very pleasing result, allowing the patient to be more active. Aesthetically, the improved breast position and contour may be very satisfactory,
and the additional scars in comparison to the benefits feel
small. Usually, one operation proves adequate for years.
OPTIONS: BREASTS For women with a small chest, perhaps there is no single group of plastic surgery patients whose self-esteem improves more with a good procedure. Despite all of the controversy surrounding breast implants, satisfying results in these women is very gratifying to both the doctor and the patient.
SILICONE VERSUS SALINE IMPLANTS
Both saline and silicone are available. Presently, the silicone implants have been approved by all relevant authorities.
Silicone implants were removed from the market because of the possible association with cancer
and connective tissue diseases. Perhaps the biggest problem with them was that they interfered with the screening mammography. The percent of silicone implants that leak also appears to be higher than previously thought. By now , however, the safety of silicone implants has been established.
Saline implants do not offer quite as natural a texture as the silicone, but can still produce
excellent results that are worry-free. The ultimate result has much more to do with the healing around the implant area than the implant itself.
TO IMPLANT OR NOT TO IMPLANT
Breast augmentation
in a 21 yr old girl, with a 300 ml, round, silicone implants Size is not the only issue with breasts- shape and contour are important, too. Some women are satisfied with having smaller breasts that are well-formed. Others consider their breasts too large or pendulous and wish a breast lift or reduction.
Every woman has to decide what fits her lifestyle. Put a pencil underneath your breast and if the pencils sticks, the breast may need some form of lifting as well as an implant. The breast lifts or reductions are fairly extensive procedures requiring three or four hours of surgery to get the breast to still match, look natural, and have fine scars.
In general with
implants, some women's chests can support larger breast than
others. Initially a small implant may be placed and
after several years, when the skin stretches, a larger
implant may be more suitable. Generally the breast can go up
two sizes, meaning that A's can go to small C's, and B's can
go to D's.
WHICH INCISION?
There are three common incisions that are used to place the implant- in the armpit, around the nipple, or underneath the breast itself. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Through the armpit, the surgeon may have trouble accurately placing the implant and dissecting out the pocket properly. The incision along the edge of the nipple may leave a fine scar and on rare occasions may interfere with breast function and sensitivity. Thirdly, when the incision is below the breast, the weight of the implant is hanging down over the scar and may cause the scar to stretch. The appearance of the breast before the surgery may be important in the surgeon's decision to use one technique or the other. For instance, in patients with a good fold underneath the breast, it may be a more appropriate place to make the incision than those that are not.
BELOW OR ABOVE THE MUSCLE
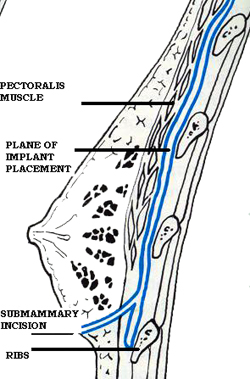
For many years, breast implants were routinely placed just below the breast tissue and over the muscles below. This muscle below the breast is called the Pectoralis Major
To prevent the formation of a scar capsule around the implant, some surgeons have found it advantageous to place the implant below the muscle. The muscle action seems to reduce the formation of scar.
Implants below the muscle
may be higher on the chest wall but they seem to stretch out
with time and drop down. Implants over the muscle may
give a more balanced look and often can look larger.
HOW ABOUT A BREAST REDUCTION?

Simple reshaping of the breast in this case. No implants have
been used!
Some of the most satisfied patients are women who have had breast reduction. Not only is the size reduced so that the person can play sports and be more active, but the nipple is elevated to a more pleasing position and the breast is repositioned higher on the chest. Usually the overall appearance of the breast is very pleasing and these are very happy patients.
IMPLANT VERSUS LIFTING
At your consultation, your doctor helps you decide if you feel breast lifting is important. An implant alone can not help a truly sagging breast but only turn it into a boggy, saggy breast.
BREAST IMPLANT COMPLICATIONS
Surgical Risk
- possible complications of general anesthesia, as well as nausea, vomiting and fever
- infection
- hematoma (collection of blood that may cause swelling, pain and bruising, perhaps requiring surgical draining)
- hemorrhage (abnormal bleeding)
- thrombosis (abnormal clotting)
- skin necrosis--skin tissue death resulting from insufficient blood flow to the skin. The chance of skin necrosis may be increased by radiation treatments, cortisone-like drugs, an implant too large for the available space, or smoking.
Implant Risks
- capsular contracture (hardening of the breast due to scar tissue)
- leak or rupture--silicone implants may leak or rupture slowly, releasing silicone gel into surrounding tissue; saline implants may rupture suddenly and deflate, usually requiring immediate removal or replacement
- temporary or permanent change or loss of sensation in the nipple or breast tissue
- formation of calcium deposits in surrounding tissue, possibly causing pain and hardening
- shifting from the original placement, giving the breast an unnatural look
-
|
|